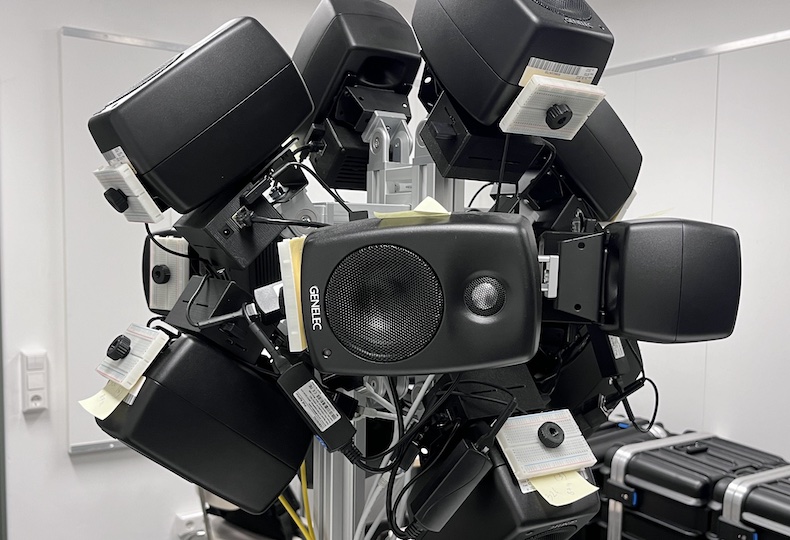
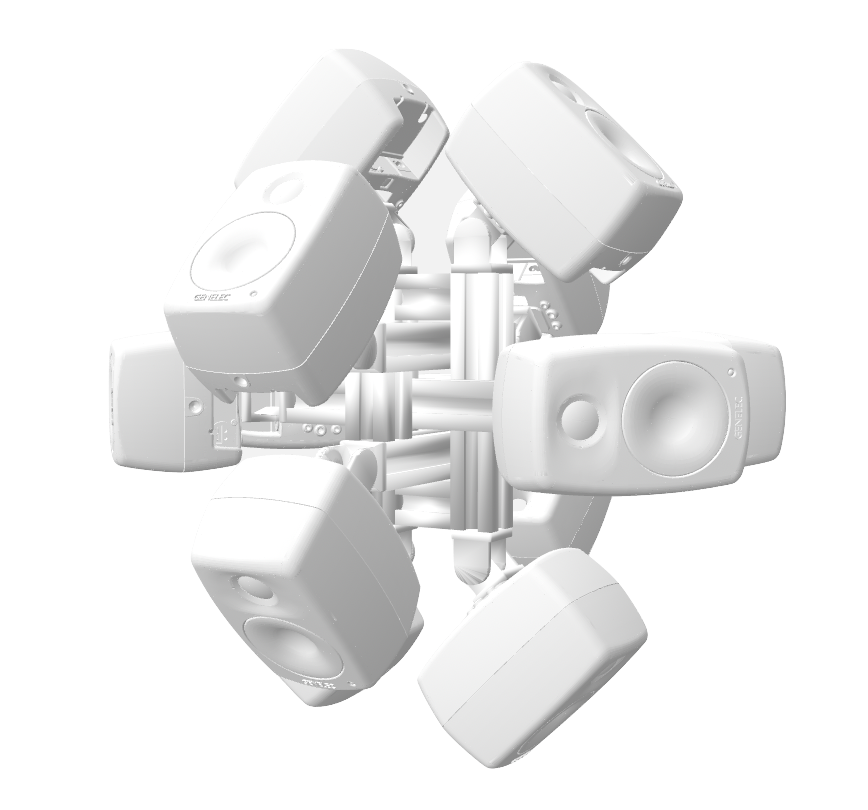
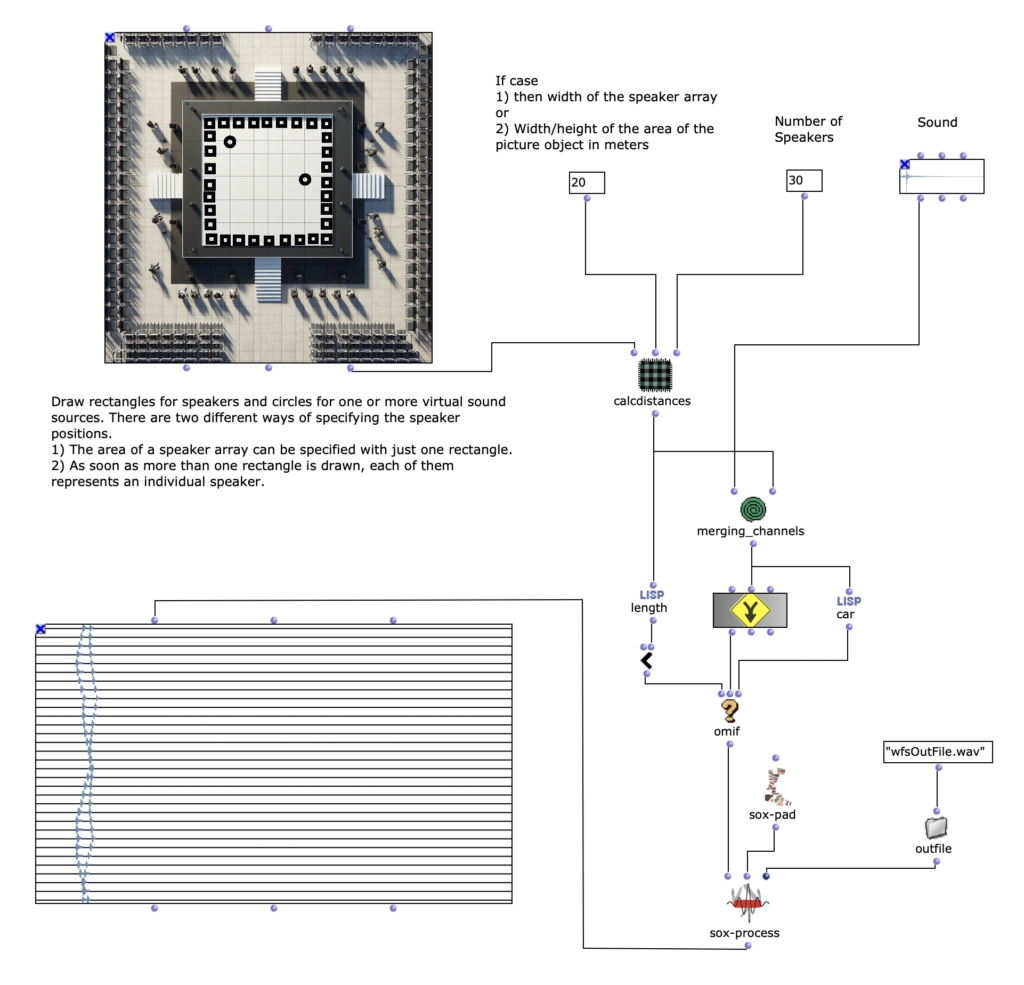
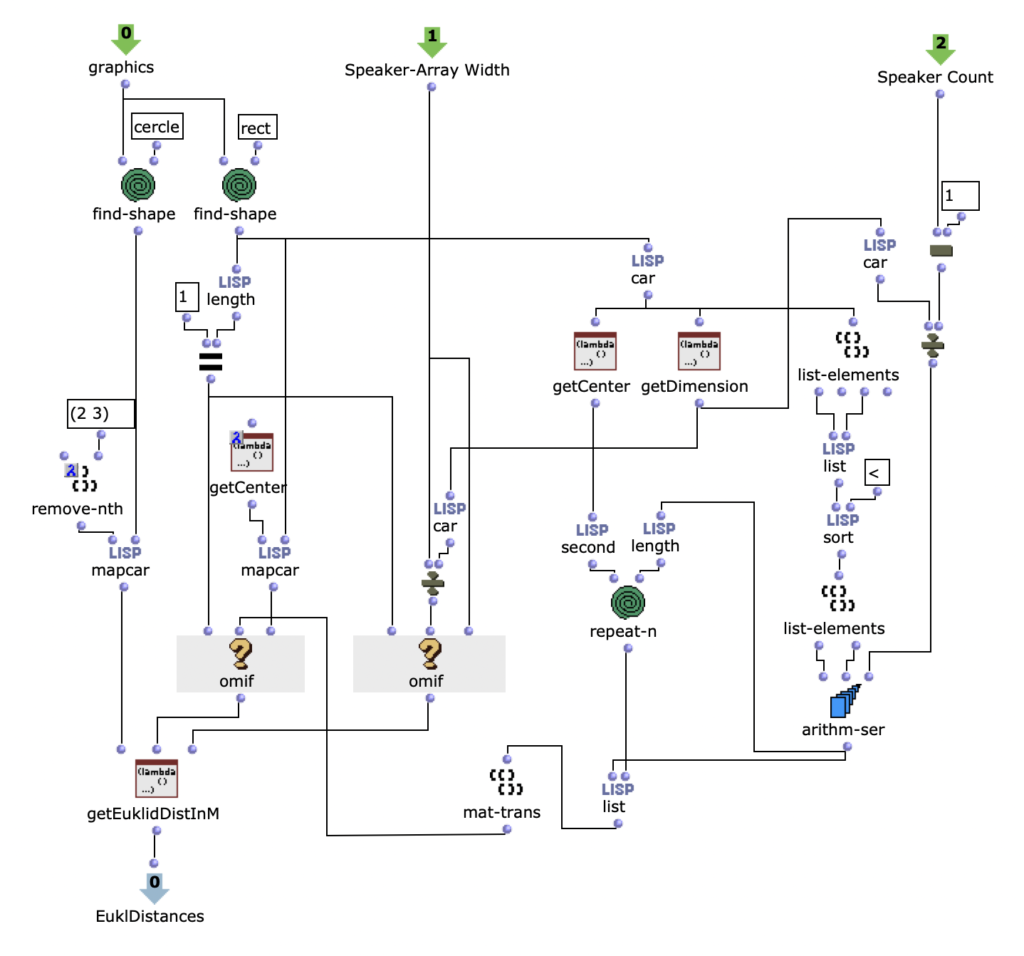
DIRAC (D_istributed I_nteractive R_adial A_udio C_luster) is a multi-purpose spatial audio device consisting of a cluster of networked loudspeakers combined with embedded computing units in a radial configuration (speakers facing outwards from each of the 12 vertices of a regular icosahedron, see Fig. 1). It has been conceived, designed and realized by Prof. Schumacher with support of music tech, mechanical engineering, IT and industrial design companies and individuals, such as RobotUnits, Augmented Instruments, Sonible. Janis Streib and Garvin Schultheiß. It can be considered a hybrid device between compact-spherical speaker array, interactive sound sculpture and multichannel loudspeaker arrangement.
Background:
Today’s use of loudspeakers in contemporary music is so commonplace that it can be virtually considered an integrated part of the instrumental catalogue of electroacoustic composers and sonic artists. Although approaches to their artistic use are manifold, they can be categorized along a continuum between its function as a sounding object with an intended distinct sonic identity and directivity pattern (sound radiation) to their use as a acoustically neutral element of an array of speakers often in a surrounding configuration to create a sonic envelopment or projection (sound projection). While former approaches often consider the loudspeaker as a component embedded within and interacting with its surrounding environment (e.g. wall reflections, etc.), in latter approaches the intention is often to minimize or “neutralize” acoustic interactions with the room – which are often considered unintended sound reproduction artefacts.
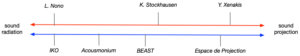
Illustration of a continuum from sound radiation to sound projection. Upper line represents artistic practices, lower line represents technical developments and installations.
DIRAC was born from the idea to develop a flexible framework and technological infrastructure, which is supportive of using individual speakers like instruments with their distinct acoustic signatures, as a generic radial sound projector (for reproduction of sound directivity patterns), and for interdisciplinary sonic art/installation contexts. Its audio rendering capabilities can range from synthesis and reproduction of channel-based material (in the tradition of sound diffusion), up to ambisonics rendering and acoustic beamforming. There is today a notable body of research into spherical loudspeaker arrays (some of them targeting commercial markets, see References below), however most developments are either lab prototypes relying on custom components and special hardware; or proprietary products, relying on third-party support and maintenance.
Rather than building on a one-size-fits-all solution, which might be costly to build, restrictive in its adaptability and difficult to maintain and extend, here key factors were modularity (adaptability for research and artistic purposes), sustainability via interchangeability of components (using off-the-shelf commercial hardware), and extensibility.
To optimize flexibility our design is based on the concept of “audio nodes” combining audio sinks (loudspeakers) with computing units (that are aware of their surrounding by sharing sensor data and other information) communicating in a distributed network cluster, using open standards and computing platforms. To minimize installation time and facilitate artistic practice we aimed to keep the necessary technical infrastructure and logistic effort to a minimum.
Accordingly, rather than developing custom hardware, the design is built on technologies from ubiquitous computing and smart device fields, in order to keep the necessary technical infrastructure and logistic effort to a minimum while providing the necessary functionalities that allow the cluster to adapt itself to conditions of its surrounding environment (e.g. for sound projection purposes) and to facilitate artistic practices involving human-computer or other forms of interaction.
Mechanical Structure and Mounts
For building the mechanical support structure and mounts, CNC-machined aluminum profiles from robotics and machine engineering domains are employed due to their modularity, precision manufacturing, extensibility (construction kit system), light weight, and convenient cable management. Below are figures illustrating the designs of the support structure.
In order to synthesize directivity patterns it is convenient to use compact spherical loudspeaker arrays in the shape of platonic solids, due to their symmetrical geometric properties, not favouring certain regions/directions. A common approach for directivity synthesis is using spherical harmonics which can be combined in order to produce multiple sound lobes in specific directions. Previous research has determined that a configuration of 12 regularly placed speakers on a sphere (dodecahedron) provides the best compromise among the platonic solids between number of channels, sound power and complexity of the controllable patterns.
Although arbitrary arrangements are technically possible (such as a dodecahedric setup), we opted for a configuration where speakers are placed at the corners of three mutually perpendicular golden-ratio rectangles (the vertices of an icosahedron) to provide a maximum of flexibility, as the symmetrical speaker configuration allows for reproduction of various audio reproduction formats, including horizontal (stereo, quad, hexaphonic) and periphonic formats (cube/hexahedron).
NB: prototypes for different numbers of nodes in various geodesic configurations exist (e.g. hemispherical, icosahedric, etc.).
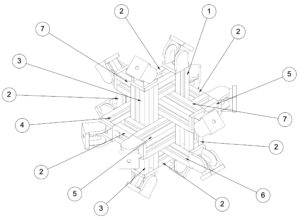
Fig. 2: Technical Drawing of Aluminum Structure and Mounts at the Vertices of a Regular Icosahedron.
Tech Configuration and Connectivity
Each cluster “node” consists of a Smart IP Speaker unit (digital loudspeakers with programmable DSP units) and a dedicated embedded computer (BELA or Raspberry Pi) mounted to the speaker via custom 3D-printed casing, offering additional processing and connectivity to various peripherals (microphones, sensors, transducers, etc.), all connected to a shared DANTE and local area network for transmission of audio signals and generic communication. To facilitate electrical circuit design 3D-printed custom mounts for breadboards were developed. In its current configuration it is using 12 Genelec 4410A smart speakers and respective embedded computers, all connected via Netgear AV Line switches, delivering Power-Over-Ethernet, Audio, Configuration, and Network communcation via a single ethernet cable. Fig. 4 shows an early prototype DIRAC setup (breadboards were added in a later design stage).
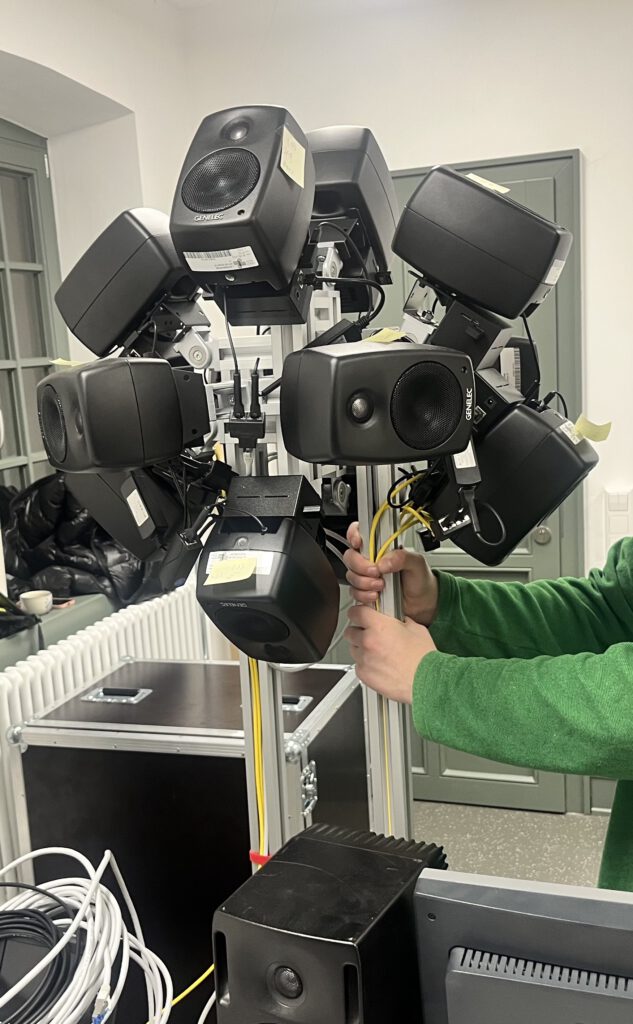

Fig. 4: Photographic Image of DIRAC on vertical support structure. Humand hands/arms shown for scale.
Control and Current Developments
Besides proprietary software (SmartIP Manager by Genelec) the internal DSP settings can be configured via an API. Current developments for a generic, opensource networking software with auto discovery and management features using generic OpenSoundControl messaging are ongoing (see this git repository). In addition, since both Dante and AES67 are supported for audio-over-ip transmission, there are current developments to add support for both BELA and RaspberryPis to extend/interact with the audio network using additional transducers (microphones, audio exciters, etc.), see this and this repository. There are also ongoing developments to integrate sensing for making the cluster aware of its surroundings, e.g. via proximity sensing, see this repository.
Audio Rendering
We are currently evaluating and experimenting with a number of different approaches: channel-based material (using direct loudspeaker feeds), panning/spatialization algorithms, such as VBAP, DBAP, etc. , Ambisonics (e.g. using Allrad Decoders), Virtual Microphones and Beamforming. In combination with networked sensing this allows covering a wide array of applications, from adaptive rendering to interactive synthesis.
Related Literature:
- Pasqual, A. M., Arruda, J. R., & Herzog, P. (2010, May). A comparative study of platonic solid loudspeakers as directivity controlled sound sources. In Proceedings of the second international symposium on Ambisonics and spherical acoustics.
- Pasqual, A. M. (2010). Sound directivity control in a 3-D space by a compact spherical loudspeaker array (Doctoral dissertation, Universidade Estadual de Campinas)
- Avizienis, R., Freed, A., Kassakian, P., & Wessel, D. (2006, May). A compact 120 independent element spherical loudspeaker array with programable radiation patterns. In Audio Engineering Society Convention 120. Audio Engineering Society
- Freed, A., Schmeder, A., & Zotter, F. (2008). Applications of environmental sensing for spherical loudspeaker arrays. IASTED Signal and Image Processing
- Schmeder, A. (2009, June). An exploration of design parameters for human-interactive systems with compact spherical loudspeaker arrays. In Proceedings of the Ambisonics Symposium.
- Farina, A., & Chiesi, L. (2016, May). A novel 32-speakers spherical source. In Audio Engineering Society Convention 140. Audio Engineering Society